The Term Used to Describe Dna Dependent Dna Polymerization Is
Previously we performed biochemical characterization of the human L1 ORF2 protein with reverse transcriptase RT activity referred to as L1 RT expressed in baculovirus-infected insect cells. Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates are the substrate as well as the energy provider for the replication process.

The Biotechnology Revolution Pcr And Cloning Expressed Genes Learn Science At Scitable
DNA Polymerase Definition DNA Polymerases are a group of enzymes that catalyse the synthesis of DNA during replication The main function of DNA polymerases is to duplicate the DNA content of a cell during cell division.
. DNA polymerase 1 also known as Kornberg enzyme has only 1 subunit made up of 928 amino View the full answer. Adenosine Deaminases Acting on tRNA C-to-U LINE. Short interspersed nuclear element.
Base-Pairing Underlies DNA Replication and DNA Repair. The effect of degree of polymerization of trehalose-based cationic polymer on DNA condensation ability was studied and it was determined that D p is not directly related to DNA complexation efficacies protection and release as determined by isothermal. But the other strand the lagging strand must be built in segments that.
During this process DNA polymerase reads the existing. Adenosine Deaminase Acting on RNA A-to-I ADAT. In fact an entire industry based in large part on this concept played an enormous role in the development of our civilization.
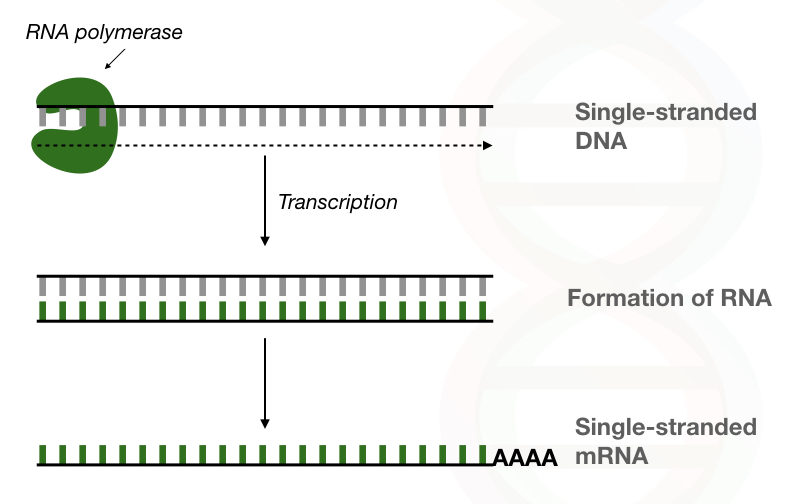
A viral DNA polymerase or reverse transcriptase RT enzyme is responsible for synthesis of DNA complementary to an RNA or DNA template. Once it reaches the terminator sequence the process terminates and the newly synthesised RNA strand is released. The DNA-dependent RNA polymerase binds to the promoter and catalyses the polymerization in the 5 to 3 direction on the template strand.
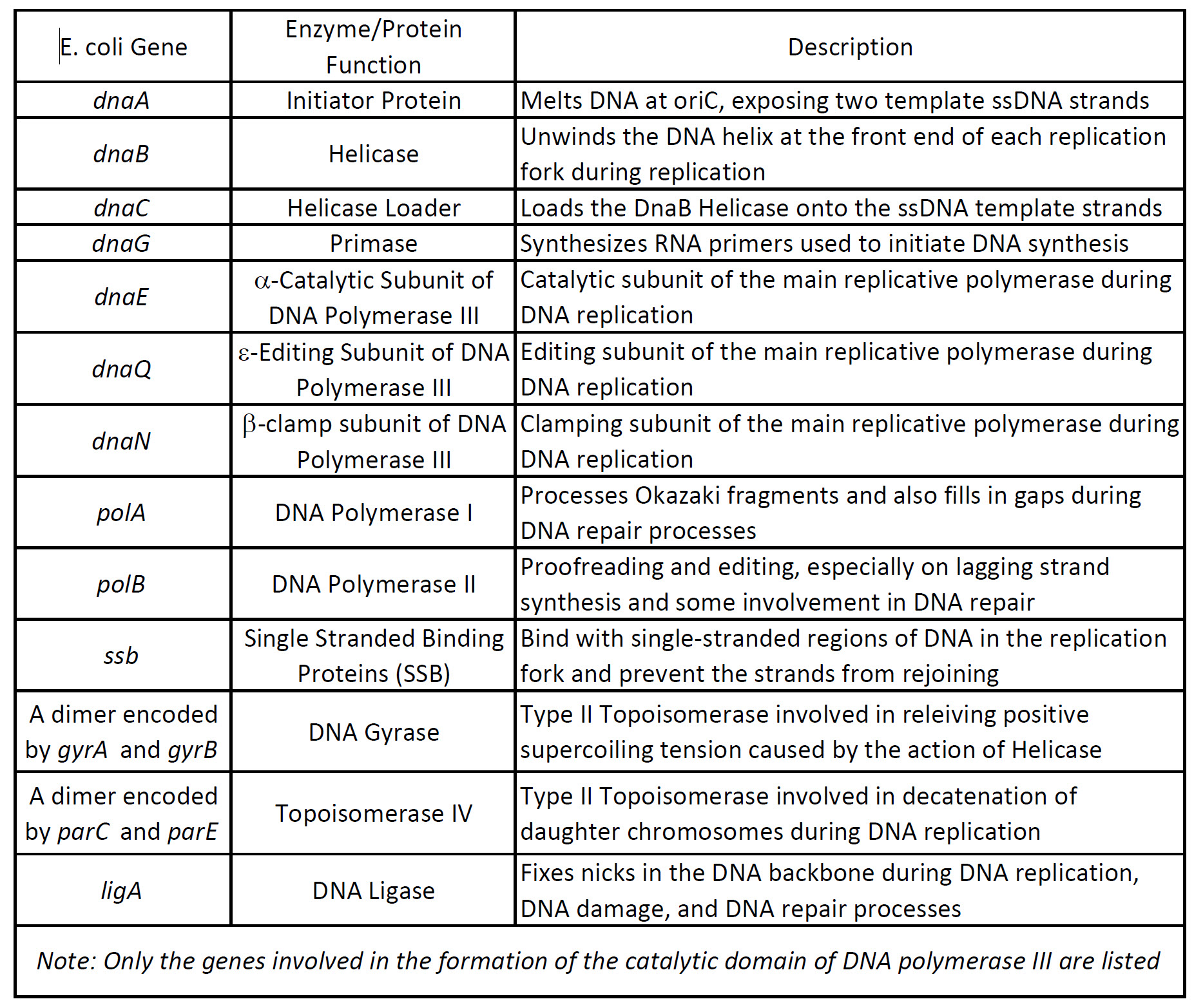
Okazaki fragments are small segments of DNA that form on the lagging strand during DNA replication. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create two identical DNA duplexes from a single original DNA duplex. Narain in Polymers and Nanomaterials for Gene Therapy 2016 433 Effect of degree of polymerization Dp.
We find and describe. The DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity of L1 RT described here directs efficient polymerization on L1 DNA. A DNA-dependent RNA polymerase-these build RNA primers associated with replication-provides the free 3 end that DNA polymerase needs for synthesizing DNA.
-A special type of gel is used for DNA electrophoresis to minimize the effects of charge-The shape of the DNA fragments has an even greater effect on movement than size or charge so charge is relatively unimportant-DNA moves toward a positive charge due to the negative charge on its phosphate groups. The polymerization of RecA on individual double-stranded DNA molecules is studied. Molecular BiologyDNA as Genetic Material and DNA Replication A.
Because DNA-dependent DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to the 3 end of a growing nucleotide chain the leading strand is built in a continuous sequence. Complementarity in a genetic sense refers to the polymerization of nucleotides in DNA. A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates the molecular precursors of DNA.
In the present study we describe the properties of DNA- and RNA-dependent DNA synthesis catalyzed by the L1 RT on the L1 templates in vitro. Answer DNA replication machinery and enzymes process of replication requires a set of catalysts enzymes 1 The main enzyme is DNA dependent DNA polymerase as it uses DNA as template to catalyses the polymerization of deoxynucleotides. The process of DNA polymerization is dehydration synthesis catalyzed by a DNA-dependent DNA polymerase.
As L1 RT lacks RNase H activity intact L1 mRNA in the heteroduplex apparently serves a stabilization factor during generation of first strand DNA and later is either cleaved by cellular RNases or displaced by L1 RT during second strand DNA synthesis. What is this. DNA viruses replicate their genomes using DNA-dependent DNA polymerases also called DNA polymerases and transcribe mRNA using DNA-dependent RNA polymerases also called RNA polymerases.
It is a part of DNA replication but does not constitute all of the reactions that are required for in vivo DNA replication. Bioinformatics is a discipline involved in the development of both hardware and software for processing storing and retrieving nucleotide and protein data. The elongation caused by RecA assembly is measured in the presence of ATP and ATPγS.
DNA polymerase or DNA dependent DNA polymerase 1 and 3 both are found in eubacteria such as Ecoli. FALSE True or False. DNA as Genetic Material Before people used words such as genetic material the concept behind this term was well established.
Not surprisingly the reverse transcriptionDNA polymerization step in HIV replication was immediately considered as a prime drug target and the nucleoside analog AZT zidovudine ZDV 3 4 was approved as the first anti-AIDS drug. Since the DNA-dependent CeNA polymerization and the CeNA-dependent DNA polymerization is possible to a limited extend we suggest CeNA as an ideal candidate to use in. Long interspersed nuclear element SINE.
DNA-dependent DNA polymerase It helps in the polymerisation catalyses and regularises the whole process of DNA replication with the support of other enzymes. DNA-dependent RNA polymerase RNApol. Our analysis is based on previously published DNARNApeptide sequencing data of the different variants from different tissues Xuan et al 2014 Xuan et al 2016.
In this report we describe hypotheses we have developed from phylogenetic analyses of CSP genes and RNA variants of the silkworm moth Bombyx mori. A linear DNA λ DNA 485 Kb anchored at one end to a cover glass and at the other end to an optically trapped 3-μm diameter polystyrene bead serves as a template. As discussed briefly in Chapter 1 DNA templating is the process in which the nucleotide sequence of a DNA strand or selected portions of a DNA strand is copied by complementary base-pairing A with T and G with C into a complementary DNA sequence This process entails the recognition of each nucleotide in the.
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase ADAR. Transcription Unit is a stretch of a DNA transcribed into an RNA molecule. 2 Replicat View the full answer.
They do so by adding nucleotides at 3-OH group of the growing DNA strand. Both of them perform polymerization activity from 5 to 3. RNA viruses have RNA genomes which can also be either double-stranded dsRNA or single-stranded ssRNA.

Rna Polymerase I An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Dna Polymerases Structural Diversity And Common Mechanisms Journal Of Biological Chemistry
Chapter 9 Dna Replication Chemistry

Dna Polymerase An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Dna Polymerase Structure Types And Functions

So Many Dna Polymerases So Little Time Goldbio
Chapter 9 Dna Replication Chemistry

Dna Polymerase An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Comparison Between Dna Polymerase Vs Rna Polymerase

Dna Directed Dna Polymerase An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

22 The Viruses Biology Libretexts

Rna Directed Dna Polymerase An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Difference Between Dna And Rna Polymerase Definition Replication Transcription Process

Okazaki Fragments An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Chapter 9 Dna Replication Chemistry

22 The Viruses Biology Libretexts

Reverse Transcriptase An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Dna Polymerase Iii Holoenzyme An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Comments
Post a Comment